What are oral solid dosage (OSD) forms in pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals? Capsules, tablets, and powders are the most common types. According to the industry report, OSD forms make up about 70% of all preparations. Tablets represent a larger portion, about 70%-80%, of the OSD forms in the market.

As technology develops, tablet manufacturing can be done using several methods, such as
- Dry granulation
- Wet granulation
- Direct compression.
Of these three methods, the direct compression method is the most straightforward and efficient. Looking to produce tablets in a simpler yet faster way? This method might be a good choice. Keep reading, and all your questions about the direct compression of tablets will be solved today.
What is the Direct Compression of Tablets?
Direct compression method is a popular way to make tablets in today's pharmaceutical industry. It compresses the mixture of active ingredients and direct compression excipients directly into tablet form. This direct compression method skips additional steps like making granules first, which is common in other methods. The ingredients used must flow well and be easy to compress. This makes the direct compression process faster, reduces steps, and cuts costs.

This direct compression method is especially good for ingredients that can be compressed directly or don't handle heat or moisture well. With few manufacturing steps, direct compression method is easier to control and cost-effective. More and more manufacturers are adopting this resource-saving tablet production method.
What are the Steps in the Direct Compression Process?
The direct compression process involves a few key steps. Though the entire process is straightforward, each step is critical to successful tablet manufacturing.
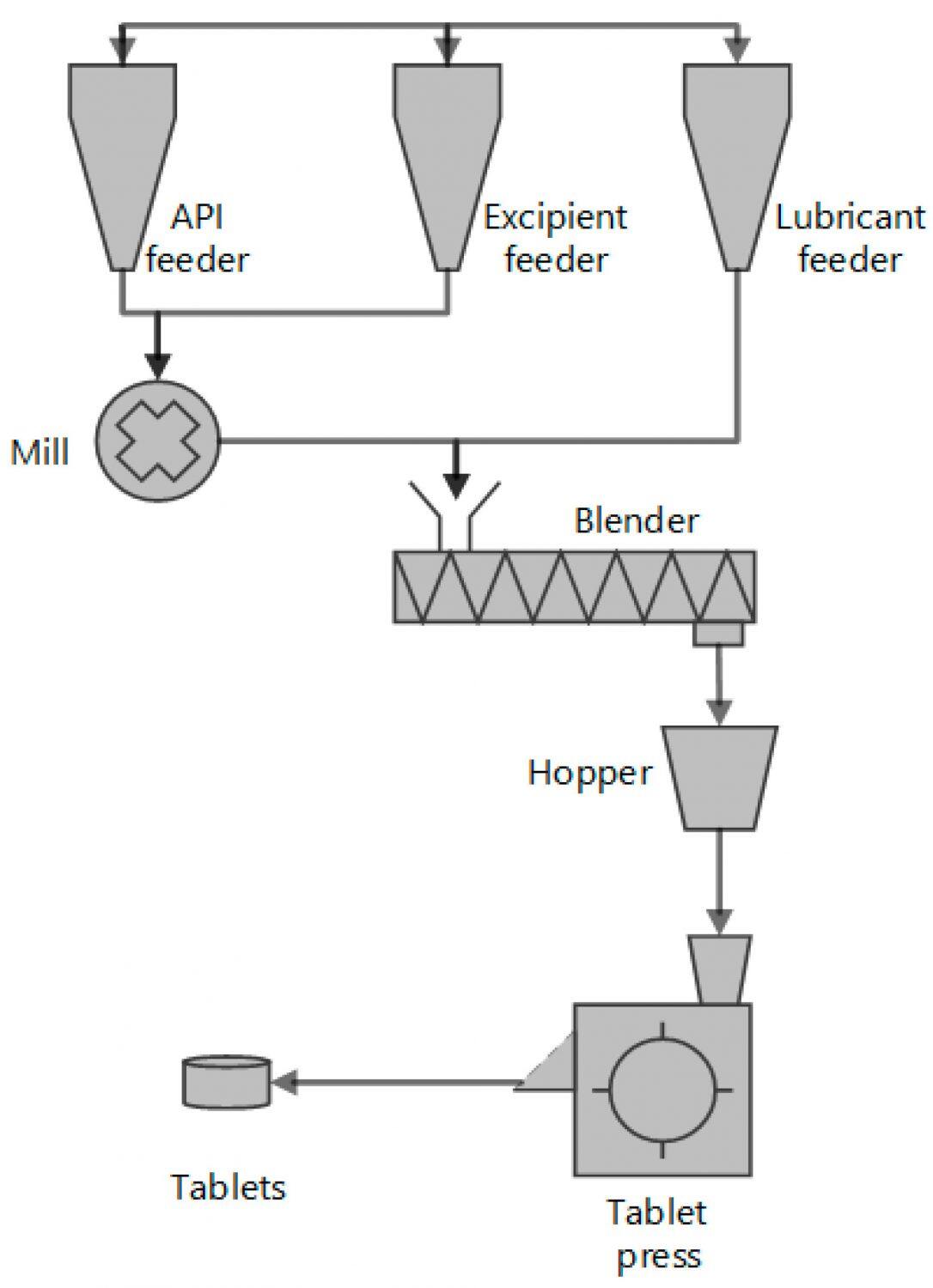
STEP 1: Milling (Optional)
This step is not always required. When the particle size of your active ingredients and direct compression excipients is too large, it is necessary to grind them using raw equipment to reduce the particle size. This allows the raw materials to flow better. Additionally, materials with a uniform particle size help create a homogeneous mixture in the following step. Of course, if you already have properly sized active ingredients and direct compression excipients, you can skip this step.
STEP 2: Blending
This step involves thoroughly mixing the powered active ingredients with the right direct compression excipients to create a homogeneous blend. Uniform distribution of these ingredients within the blend is essential for consistent tablet potency.
STEP 3: Filling
The blend is then fed into a tablet compression machine. The pill pressing machine comes with one or multiple die cavities for forming tablets. These cavities are then filled with the blend. The filling volume is controlled by the machine.
STEP 4: Compression
This is the most important step of the direct compassion of tablets. The blend within the cavities is then compressed into tablets using tableting tooling. The tablet compression machine applies high pressure onto the tooling to compact the powdered ingredients into solid tablets.
STEP 5: Ejection
The tooling within the machine typically includes an upper punch, a lower punch, plus a die. This step uses the lower punch to push the formed tablet out of the die cavity.
Different Excipients Used in Direct Compression of Tablets
As mentioned above, excipients are essential in a tablet direct compression formulation. During the direct compression process, they are added to ensure you get high-quality final products. Common direct compression excipients used in the direct compression of tablets are:

1. Binders. These direct compression excipients help hold all ingredients together. This helps keep the tablet from splitting. Some common binders include MCC, HPC, and HPMC.
2. Fillers (Diluents). Fillers add bulk to the tablet. If your tablet contains few active ingredients, these direct compression excipients can increase the bulk of the tablet. Examples include lactose, mannitol, and dicalcium phosphate.
3. Disintegrants. These allow the tablet to break down right in the stomach. You might find sodium starch glycolate or crospovidone in your tablet for this purpose.
4. Lubricants. These direct compression excipients are used to reduce friction. They enable all ingredients and the finished tablets to travel through the tablet press smoothly. Magnesium stearate and stearic acid are popular choices.
5. Glidants. Think of these as the flow helpers; they make sure the powder blend flows well into the die cavities. Silicon dioxide is a common glidant.
6. Anti-adherents. These stop the powder blend from sticking to the tableting tooling. Talc is often used for this, and it can also double as a lubricant.
REMINDER: Be sure to choose the right direct compression excipients that work well with the active ingredients. This will ensure the tablet is stable and effective.
Advantages of Direct Compression Method
Direct compression offers several notable benefits:
- It's an easy, straightforward process with fewer steps compared to granulation methods. This makes tableting quicker and less complicated.
- By cutting out the steps like granulation and drying, it saves both time and money. If you're handling large-scale operations, this efficiency can be a big plus.
- Sensitive active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) benefit from this method because they don't have to be exposed to moisture and heat during the direct compression process. This will bring you stable and effective tablets.
- It reduces the risk of contamination because all ingredients will go through fewer steps and come in contact with less equipment.
Disadvantages of Direct Compression Method
However, direct compression of tablets also presents some challenges:
- Direct compression of tablets requires excipients, but not all work well in this method. Finding the direct compression excipients that optimize the tablet formulation for a successful compression can be challenging.
- Direct compression excipients are actually inactive ingredients. That is to say, the APIs and excipients have different properties. So, creating a uniform blend of these ingredients is often tricky.
- There is also a difference between the APIs and direct compression excipients in terms of density. This factor can lead to the segregation of these ingredients. For instance, if they're dry powders, chances are that static charges will be induced during the blending stage. This will cause uneven distribution of the APIs in the tablet.
- Many direct compression excipients are protected by patents. If you're using some hard-to-replace options, you have to bear a higher price tag.
Direct Compression vs. Dry Granulation vs. Wet Granulation
Direct compression and granulation (wet and dry methods) are the two main tableting techniques. What are the differences among them? Let's compare them side by side.
| Factor | Direct Compression | Dry Granulation | Wet Granulation |
| Process | Simple, involves fewer steps | Involves compacting powder into slugs | Involves mixing with liquid, wet massing, and drying |
| Time & Cost | Quick and cost-effective | Moderate time and cost | Time-consuming and costly due to multiple steps |
| Stability | Good for moisture and heat-sensitive APIs | Better stability compared to wet granulation | Less suitable for moisture-sensitive APIs |
| Powder Requirements | Requires good flow and compressibility | Improves compressibility with fewer excipients | Can handle powders with poor compressibility |
| Scalability | Easily scalable | Moderate scalability | Highly scalable |
| Uniformity | Uniformity depends on excipient choice | Good uniformity | Excellent uniformity |
| Typical Use | Simple formulations, heat/moisture-sensitive APIs | Low compressibility APIs, moisture-sensitive | APIs requiring uniform granulation and strong tablets |
FAQs on Direct Compression of Tablets
Q: How does particle size affect direct compression?
A: Particle size matters because uniform particles improve flow and compression to create consistent solid tablets. Particle size variations can cause uneven blending and affect tablet quality.
Q: Can direct compression handle high-dose tablets?
A: Direct compression may not be suitable for producing high-dose tablets. The direct compression method can't compress a large amount of active ingredients effectively. Also, with high doses, it's not easy to bind everything together well simply by compression.
Q: What are the considerations when selecting direct compression excipients?
A: Look for direct compression excipients that compress well, flow smoothly, and are compatible with the APIs. They should also aid in proper tablet disintegration and dissolution without causing chemical reactions with the APIs.
Q: What is the impact of compression force on tablet quality?
A: Tablet compression force determines the density and hardness of the tablets. Too much force can make tablets too hard and prone to defects. Too little can result in weak, fragile tablets. It's crucial to control the tablet compression force for optimal tablet quality.
Final Thoughts
Direct compression of tablets is simple and efficient. This method is worth a try whether you're producing medicines or supplements. By using the right tablet press machine and applying the proper tablet compression force, you can get high-quality tablets. In a word, direct compression is a valuable process in the pharma world. For more details about this popular tableting technique, feel free to contact us today!